Apple has quietly eliminated “carbon neutral” branding from its latest device releases worldwide, marking a significant retreat from environmental marketing claims that dominated the company’s messaging just two years ago. Our expert team has analyzed this strategic shift to help you understand how legal challenges and regulatory pressure are reshaping how tech companies communicate their environmental initiatives.
Our methodology involves examining court documents, regulatory frameworks, and corporate environmental reporting changes. Every aspect analyzed provides insights into the evolving landscape of environmental marketing and what these changes mean for consumer decision-making.
Key Analysis Areas:
- Legal challenges driving marketing policy changes
- European Union regulatory impact on global strategies
- Carbon offset project scrutiny and transparency requirements
- Corporate environmental communication evolution
- Consumer protection against misleading environmental claims
We continuously monitor environmental marketing regulations and corporate policy shifts to provide comprehensive analysis of how legal and regulatory developments affect technology companies’ environmental messaging.
Strategic Impact Overview:
- Legal Compliance Leader: Court rulings reshape environmental marketing
- Regulatory Response Specialist: EU directives drive global policy changes
- Environmental Strategy Analyst: Offset project limitations exposed
Each assessment includes detailed examination of legal precedents, regulatory requirements, and corporate strategic responses to changing environmental marketing landscapes.

Legal Compliance Leader: German Court Decision Creates Global Impact
Apple’s removal of carbon neutral labeling stems from a Frankfurt Regional Court ruling in August 2025 that found the company’s environmental claims misleading to German consumers, triggering worldwide marketing policy changes.
Court Ruling Analysis: The German court determined that Apple misled consumers by claiming carbon neutrality while relying on forestry offset projects in Paraguay with lease agreements expiring in 2029. This timeline falls significantly short of the 2050 period consumers would reasonably expect for genuine carbon neutrality achievements.
Legal Challenge Origins: Deutsche Umwelthilfe (DUH), a German environmental organization, initiated the legal action by accusing Apple of “greenwashing” practices. The organization characterized the court victory as a significant win against misleading environmental marketing in the technology sector.
Offset Project Vulnerabilities: Court findings revealed that 75% of land lease agreements supporting Apple’s carbon offset initiatives lacked guarantees beyond 2029, creating uncertainty about long-term environmental impact sustainability and carbon neutrality maintenance.
Global Policy Response: Rather than maintaining different marketing strategies across regions, Apple chose unified global messaging by removing carbon neutral claims from all markets, demonstrating how localized legal decisions can drive worldwide corporate policy adjustments.
Regulatory Response Specialist: EU Directives Reshape Environmental Marketing
Apple’s proactive removal of carbon neutral claims anticipates stricter European Union regulations scheduled to take effect in September 2026, illustrating how regulatory frameworks influence corporate environmental communication strategies.
EU Directive 2024/825 Requirements: The “Directive on Empowering Consumers for the Green Transition” explicitly prohibits companies from making carbon neutrality claims based on offset projects, stating that businesses cannot assert products have “neutral, reduced or positive environmental impact” through greenhouse gas offset mechanisms.
Regulatory Timeline Impact: Apple’s decision to eliminate carbon neutral messaging ahead of the September 2026 implementation deadline shows strategic compliance planning rather than reactive policy adjustment after regulatory enforcement begins.
Cross-Border Regulatory Influence: The EU directive’s impact extends beyond European markets as multinational corporations like Apple adopt unified global policies to avoid managing different regulatory compliance requirements across various jurisdictions.
Industry-Wide Implications: These regulatory changes affect all technology companies making environmental claims, creating new standards for substantiating environmental marketing assertions and forcing greater transparency in carbon reduction strategies.

Environmental Strategy Evolution: Continued Progress Despite Marketing Changes
Apple maintains its environmental initiatives through the “Apple 2030” program while adjusting public messaging to comply with legal and regulatory requirements, demonstrating separation between operational environmental progress and marketing communication strategies.
Operational Environmental Improvements: The company has reduced total emissions by more than 60% since 2015 and continues pursuing supply chain carbon neutrality by 2030, indicating that environmental progress continues independent of marketing messaging changes.
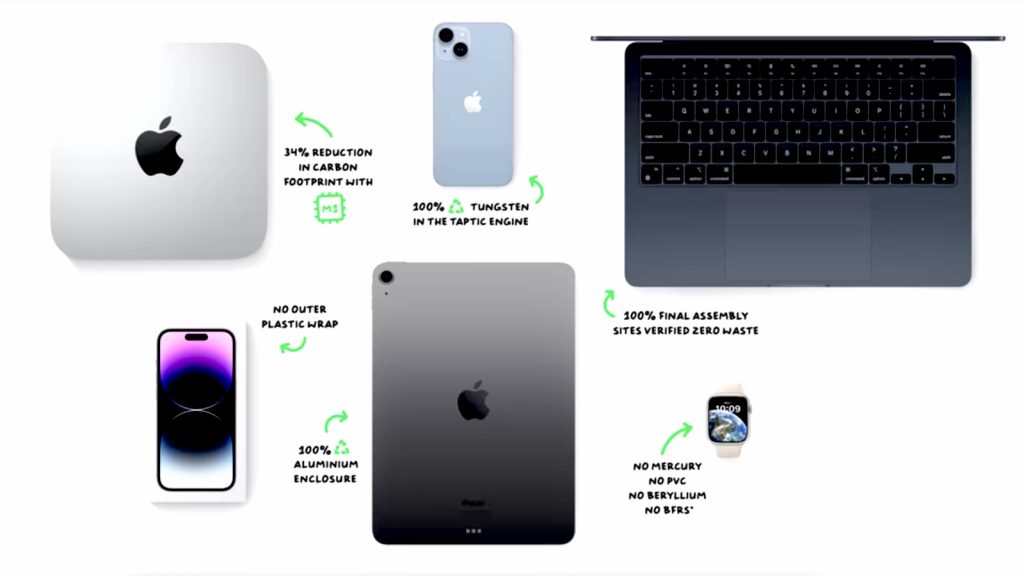
Product-Level Environmental Performance: Apple Watch Series 11 demonstrates measurable environmental improvement with emissions of 8.1 kg compared to 8.3 kg for Series 10, while maintaining significant recycled material usage including 100% recycled cobalt in batteries and recycled aluminum or titanium cases.
Documentation Strategy Adjustments: Environmental reports for new Apple Watch models no longer reference carbon neutrality, while internal documentation for M4 Mac mini maintains carbon neutrality references that have been removed from public marketing materials.
Sustainable Material Integration: New devices continue incorporating substantial recycled content across multiple components, showing that material sustainability initiatives remain priority areas despite carbon neutrality messaging elimination.
Corporate Environmental Communication Transformation
The removal of carbon neutral claims represents broader shifts in how technology companies communicate environmental initiatives as regulatory scrutiny intensifies and consumer protection agencies challenge unsubstantiated marketing assertions.
Marketing Strategy Realignment: Apple’s adjustment from bold carbon neutrality claims to specific emission reduction metrics reflects industry movement toward measurable, verifiable environmental achievements rather than aspirational marketing language.
Transparency Requirements Evolution: Legal challenges and regulatory frameworks increasingly demand detailed substantiation of environmental claims, forcing companies to provide comprehensive documentation of offset project timelines, verification methods, and long-term sustainability guarantees.
Consumer Protection Enhancement: Court decisions and regulatory directives prioritize protecting consumers from misleading environmental marketing while encouraging genuine corporate environmental responsibility through accurate, verifiable sustainability communications.
Strategic Implications for Technology Industry
Apple’s experience illustrates how legal challenges and regulatory developments reshape environmental marketing across the technology sector, creating new standards for substantiating sustainability claims and influencing industry-wide communication strategies.
Competitive Environmental Messaging: Other technology companies will likely adjust environmental marketing approaches in response to Apple’s legal challenges and regulatory compliance requirements, creating industry-wide shifts toward more conservative, verifiable sustainability communications.
Offset Project Scrutiny: The German court’s focus on offset project timelines and sustainability guarantees establishes precedents for evaluating carbon neutrality claims across the technology industry, requiring more rigorous documentation of environmental impact mitigation strategies.
Global Regulatory Harmonization: Apple’s unified global response suggests that technology companies may adopt standardized environmental messaging to comply with the most stringent regulatory requirements across all markets rather than managing region-specific compliance strategies.
Consumer Decision-Making Considerations
Apple’s carbon neutral messaging removal affects how consumers evaluate technology products’ environmental impact while actual environmental performance improvements continue through measurable emission reductions and sustainable material integration.
Environmental Impact Assessment: Consumers can still evaluate Apple products’ environmental performance through specific emission metrics, recycled material percentages, and supply chain sustainability initiatives disclosed in environmental reports despite carbon neutrality claim elimination.
Marketing Claim Evaluation: The legal challenges highlight the importance of scrutinizing corporate environmental claims and understanding the difference between marketing assertions and verifiable environmental performance improvements.
Regulatory Protection Benefits: Stricter environmental marketing regulations provide consumers with greater protection against misleading sustainability claims while encouraging companies to focus on measurable environmental improvements rather than aspirational marketing language.
Industry Environmental Marketing Evolution
Apple’s carbon neutral claim removal signals broader transformation in technology industry environmental communication as legal frameworks and regulatory requirements demand greater substantiation of sustainability assertions.
The shift from broad carbon neutrality claims to specific emission reduction metrics reflects evolving standards for environmental marketing accuracy and consumer protection. While Apple continues pursuing environmental improvements through material sustainability and emission reduction initiatives, the company has adapted its communication strategy to comply with legal requirements and regulatory frameworks.
This development illustrates how legal challenges and regulatory pressure drive corporate environmental communication evolution, potentially creating industry-wide standards for substantiating sustainability claims and encouraging focus on measurable environmental improvements rather than aspirational marketing language.




Post a comment